1. GOAL of the course
• 데이터마이닝의 기본 개념들
• 데이터 전처리 (data preprocessing)
• Association, correlation, and frequent pattern analysis
• Classification
• Cluster and outlier analysis
• Data Mining: Industry efforts and social impacts
2. Technology Trend
• Explosive growth of data : from terabytes to petabytes
↪ Big data, Internet of Things, Web2.0, Scientific simulation
• Motivation of Data Mining
↪ Information is often hidden in data, but much of the data is not analyzed at all
↪ Unprecedented amounts of data are being generated and collected (computing and storage technologies), but most of data are just kept stored
• Internet of Things , Machine-to-Machine, Smarter Planet
↪ sensors in our daily life , with wireless network
↪ Wireless Network > Sensor Streams > Data mining and knowledge discovery
• Web 2.0
↪ Web 2.0 site allows users to interact and collaborate with each other in a social media dialogue
↪ Social networking sites (Facebook, Twitter) , Blogs, Wikis, Photo/Video sharing sites
↪ Social networking sites → data is modeled using a graph
• Scientific Simulations
↪ Data-centric science: through scientific simulations and observations data is produced
↪ Empirical science → theoretical science → computational science → data science
↪ ex. NASA Center for Climate Simulation (NCCS) - satellite observational data, Particle accelerator, DNA sequencing
↪ It is very important to efficiently analyze the vast amount of data generated by observations and simulations to facilitate scientific research
3. Introduction to Data Mining
• Data mining
↪ knowledge discovery from data
↪ Extraction of interesting (non-trivial, implicit, previously unknown, and potentially useful) patterns or knowledge from huge amounts of data
↪ Exploration & analysis, by automatic means, of large quantities of data in order to discover meaningful patterns
↪ 다른 명칭 : Knowledge Discovery from data (KDD), Machine learning, Knowledge extraction
• Not Data Mining
↪ ex1. Look up phone numbers in a phone → simple searching
↪ ex2. Query a Web search engine for the information about "Amazon" → simple keyword search
↪ Simple searching is not considered as data mining
• Knowledge discovery process
↪ data mining is a part of KDD
↪ (Data) → selection → (target data) → preprocessing → (preprocessed data) → transformation → (transformed data) → Data mining → (patterns) → interpretation / evaluation → knowledge
▸ Preprocessing : Data Cleaning (noise, error), Data Integration, Feature selection
▸ Transformation : some algorithm requires a specific data format
▸ Interpretation/Evaluation: Analysis, Visualization by a human expert
• Predictive data analytics
↪ One of the topics in data mining
↪ Progression from data to insights to decisions
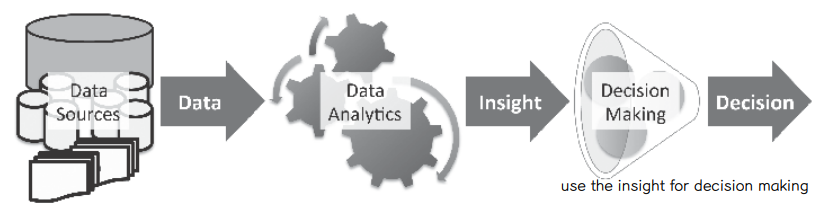
↪ Art of building and using models that make predictions based on patterns extracted from historical data
• Beginning of Data mining
↪ Dr.Rakesh Agrawal's pioneering work imid-1990s's: Association rules (e.g market basket analysis), Apriori algorithm (how often two sets of items occur), Sequential patterns

• Confluence of multiple disciplines
↪ Tremendous amount of data: higperformancece computing techniques to handle
↪ high dimensionality of data
↪ high complexity of data type: data streams and sensor data, Time-series data, sequence data, trajectory data, social network data, graph-structured data → heterogeneous data types
• sub-fields in data mining

• Data mining and privacy
↪ Data mining should NOT violate the privacy of the data owners
↪ Privacy-preserving data mining is an important direction in data mining
• 데이터마이닝 분야 저널/컨퍼런스
↪ KDD conference: KDD, ICDM, SDM
↪ Journal: IEEE, TKDE, DMKD, TKDD
4. Example
• Association Rule Discovery
↪ predict the occurrence of an item based on occurrences of other items

• Market Basket analysis
↪ An example of association rule discovery
↪ Goal: to identify items that are bought together by sufficiently many customers
↪ ex. diaper and beer
• Classification

• Direct marketing
↪ Goal: reducing the cost of mailing by targeting a set of consumers likely to buy a new product
↪ ex. 카카오톡 지그재그 메시지

• Clustering
↪ Grouping data to form new categories (clusters)
↪ 원리: maximizing intra-cluster (within) similarity and minimizing inter-cluster (between) similarity

• Document Clustering
↪ Useful to automatically group retrieved documents into a list of meaningful categories

• Outlier analysis (↔ clustering)
↪ Finding data objects that do not comply with the general behavior or model of the data
↪ To find abnormal (suspicious) behavior from the data
↪ Ex. credit card fraud detection
'1️⃣ AI•DS > 📕 머신러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 데이터마이닝 Preprocessing ③ (0) | 2023.03.29 |
|---|---|
| 데이터마이닝 Preprocessing ② (0) | 2023.03.15 |
| [05. 클러스터링] K-means, 평균이동, GMM, DBSCAN (0) | 2022.05.07 |
| [06. 차원축소] PCA, LDA, SVD, NMF (0) | 2022.04.24 |
| [05. 회귀] 선형회귀, 다항회귀, 규제회귀, 로지스틱회귀, 회귀트리 (0) | 2022.03.25 |




댓글